For your patients with positional obstructive sleep apnea
Take a closer look at positional OSA
Defining positional OSA
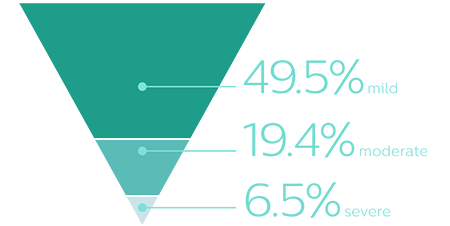
Positional OSA has been identified in many patients with OSA5
Positional OSA is a specific diagnosis in which the vast majority of apneic events occur during supine sleep.3 Positional OSA is diagnosed from any sleep study in which body position is measured. 47% of OSA patients may have exclusive positional OSA.4
Cartwright criteria uses the following to define and diagnose positional OSA3
AHIsupine ≥ 2 x AHInon-supine

Backed by clinical evidence
NightBalance is supported by years of clinical studies in patients with positional OSA.
Berry, R. et al, NightBalance Sleep Position Trainer Device Versus Auto-Adjusting Positive Airway Pressure for treatment of Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, Vol. 5, No.7, 947-956
Van Maanen et al, The sleep position trainer: a new treatment for positional obstructive sleep apnoea Sleep and Breathing (2013) 17:771–779
Van Maanen & de Vries, Long-Term Effectiveness and Compliance of Positional Therapy with the Sleep Position Trainer
SLEEP 2014; Vol. 37, No. 7
Eijsvogel etal, Sleep Position Trainer versus Tennis Ball Technique
Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine 2015; Vol. 11, No. 2
Dieljtens, A promising concept of combination therapy for positional obstructive sleep apnea
Sleep Breath 2015; 19:637–644
Benoist, Positional therapy in patients with residual positional obstructive sleep apnea after upper airway surgery
Sleep Breath 2016
Benoist, A randomized, controlled trial of positional therapy versus oral appliance therapy
Sleep Medicine 2017; 34:109e117
De Ruiter, Durability of treatment effects of the SPT versus oral appliance therapy in positional OSA: 12-month follow-up
Sleep Breath 2017
Laub, A Sleep Position Trainer for positional sleep apnea: a randomized, controlled trial
Journal of Sleep Research 2017
Our team is an extension of your team:
Customer care
Reimbursement expertise
Our top priority is to help patients obtain the equipment they need for their prescribed therapy. If you have questions contact our friendly, knowledgeable customer care team.

Call: 833-916-1041
Fax: 833-461-0791
Citations:
1. Berry, R. et al, NightBalance sleep position treatment device versus auto-adjusting positive pressure airway prssure for treatment of positional obstructive sleep apnea, J Clin Sleep Medicine,2019 ,Vol. 5, No.7, 947-956 2. NightBalance OSA Symptoms survey: Reimbursement Dossier Netherlands 3. Cartwright criteria, Effect of Sleep Position on Sleep Apnea Severity, R. Cartwright, 1984. 4. Heinzer, R. et al, Prevalence and Characteristics of Positional Sleep Apnea in the HypnoLaus Population-based cohort, Sleep Medicine 2018; 48:157-162. 5. Mador, J. et al, Prevalence of Positional Sleep Apnea in Patients Undergoing Polysomnography, Chest 2005, Volume 128, Issue 4, pages 2130-2137.6. Van Maanen et al. 2013, The sleep position trainer: a new treatment for positional obstructive sleep apnea.

